What Causes Heart Failure
Although the risk of heart failure doesnt change as you get older, youre more likely to have heart failure when youre older.
Many medical conditions that damage the heart muscle can cause heart failure. Common conditions include:
- Tobacco and recreational drug use.
- Medications. Some drugs used to fight cancer can lead to heart failure.
Point Of Maximal Impulse
The point of maximal impulse of the left ventricle is usually located in the midclavicular line at the fifth intercostal space. With the patient in a sitting position, the physician uses fingertips to identify this point. Cardiomegaly usually displaces the cardiac impulse laterally and downward.
At times, the point of maximal impulse may be difficult to locate and therefore loses sensitivity . Yet the location of this point remains a specific indicator for evaluating the size of the heart.14
Summary Of Treatment Recommendations
Patients with HFpEF and symptoms of volume overload should be treated with diuretics.31 Hypertension should be treated according to appropriate guidelines.3 Although RCTs of several medications showed fewer heart failure hospitalizations, this benefit was offset by increases in hospitalizations for other reasons. Thus, in the absence of hypertension, the evidence does not support treating patients with HFpEF with any medication except diuretics. Additionally, RCTs of angioten-sin receptor blockers, nitrates, and spironolactone raise concerns about adverse effects, and physicians should avoid using these medications, if possible.18,2325 Similarly, physicians should avoid the use of digoxin in patients 65 years and older.27 Physicians should consider referring patients with HFpEF who can exercise safely for exercise training or cardiac rehabilitation. Comorbid atrial fibrillation or CAD should be treated.
Recommended Reading: Why Is My Resting Heart Rate Going Up
Tests To Measure Your Ejection Fraction
Your provider may order an echocardiography or other imaging tests to measure your ejection fraction. Your ejection fraction is the percent of the blood in the lower left chamber of your heart that is pumped out of your heart with each heartbeat. Ejection fraction measures how well your heart pumps. This helps diagnose the type of heart failure you have and guides your treatment.
- If 40% or less of the blood in your left ventricle is pumped out in one beat, you have heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
- If 50% or more of the blood in your left ventricle is pumped out in one beat, you have heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
- If your ejection fraction is somewhere in between 41% to 49%, you may be diagnosed with heart failure with borderline ejection fraction.
Rest Exercise And Exercise Training
Rest
In acute heart failure or destabilization of CHF, physical rest or bed rest is recommended.
Exercise
Exercise improves skeletal muscle function and therefore overall functional capacity. Patients should be encouraged and advised on how to carry out daily physical and leisure time activities that do not induce symptoms. Exercise training programs are encouraged in stable patients in NYHA class IIIII. Standardized recommendations for exercise training in heart failure patients by the European Society of Cardiology have been published.
Read Also: Why Do I Have Heart Palpitations
Heart Failure Diagnosis Criteria: Steps To Diagnosis Heart Failure
To know about Heart Failure diagnosis criteria, you must first learn about the conditions. Heart failure undoubtedly is the most dangerous condition of the human heart. As the riskiest condition of the sensitive organ, heart failure treatment is slightly acute in the modern age.
But yet, specialists carefully follow the patients early medical history, health condition, and other diseases, and finally review all the symptoms of heart failure before diagnosis. To know clearly about all the criteria doctors and specialists maintain to diagnose heart failure conditions, continue reading to the next.
Jump to…
Suggested Approach To Diagnosis
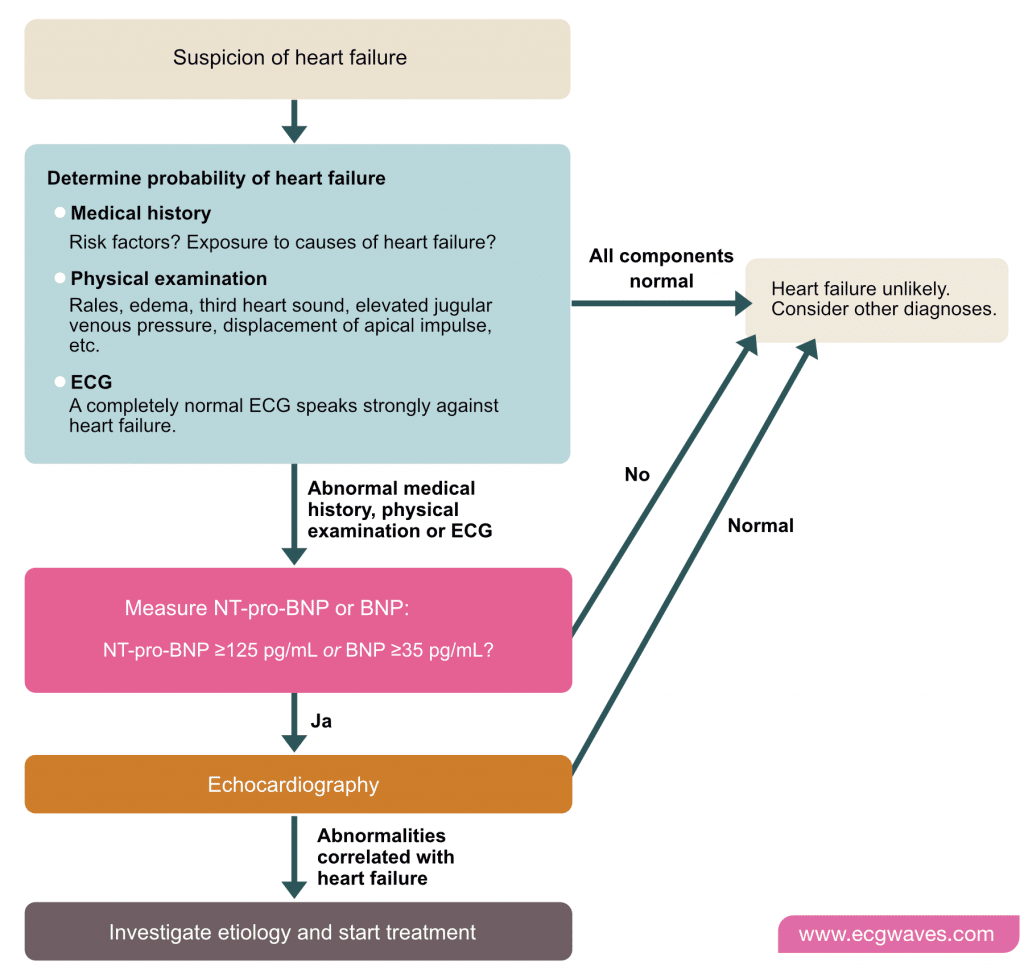
Patients presenting with symptoms concerning for heart failure should undergo clinical evaluation. If physical examination findings suggest heart failure or fulfill the clinical criteria for the MICE or Framingham rules, the patient should be referred for TTE.3,5 BNP or NT pro-BNP should be measured in patients who do not meet these criteria, and the patient should be referred for TTE if the BNP level is 35 pg per mL or greater, the NT pro-BNP level is 125 pg per mL or greater, or the score on the Netherlands rule is 13 or greater. TTE assessment of LVEF and diastolic function can confirm HFpEF5 .
Recommended Reading: How To Calculate Your Resting Heart Rate
Calculating And Interpreting The Hfapeff Score
Each domain can add maximally 2 points if any major criterion from this domain is positive or 1 point if no major but any minor criterion is positive. If several major criteria within a single domain are positive, this domain adds 2 points and if no major but several minor criteria are positive it gives still 1 point. Major and minor criteria are not additive in a single domain. Points can be added just when they originate from different domains.
A total score of 5 points is considered to confirm the HFpEF while a score of 1 point is considered to make a diagnosis of HFpEF very doubtful and to mandate further investigations for alternative causes. If the patient has an intermediate score further evaluation should be done. .
Summarizing the new data, echocardiographic criteria for HFpEF can be divided into structural and functional .
|
Table 2 Step 2 : Echocardiographic and Natriuretic Peptide Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction Workup and Scoring System |
Symptoms And Signs In The Diagnosis Of Heart Failure
Breathlessness, ankle swelling, and fatigue are the characteristic symptoms and signs of heart failure but may be difficult to interpret, particularly in elderly patients, in obese, and in women. It should be interpreted carefully and different modes should be assessed.
-
Symptoms and signs are important as they alert the observer to the possibility that heart failure exists. The clinical suspicion of heart failure must be confirmed by more objective tests particularly aimed at assessing cardiac function .
Fatigue is also an essential symptom in heart failure. The origins of fatigue are complex including low cardiac output, peripheral hypoperfusion, skeletal muscle deconditioning, and confounded by difficulties in quantifying this symptom.
Peripheral oedema, raised venous pressure, and hepatomegaly are the characteristic signs of congestion of systemic veins., Clinical signs of heart failure should be assessed in a careful clinical examination, including observing, palpating, and auscultating the patient.
Recommended Reading: Most Common Heart Surgery
Tests For Heart Failure
Tests you may have to diagnose heart failure include:
- blood tests to check whether there’s anything in your blood that might indicate heart failure or another illness
- an electrocardiogram this records the electrical activity of your heart to check for problems
- an echocardiogram a type of ultrasound scan where sound waves are used to examine your heart
- breathing tests you may be asked to blow into a tube to check whether a lung problem is contributing to your breathlessness common tests include spirometry and a peak flow test
- a chest X-ray to check whether your heart’s bigger than it should be, whether there’s fluid in your lungs , or whether a lung condition could be causing your symptoms
You can read more about tests for heart conditions on the British Heart Foundation website.
Myocytes And Myocardial Remodeling
In the failing heart, increased myocardial volume is characterized by larger myocytes approaching the end of their life cycle. As more myocytes drop out, an increased load is placed on the remaining myocardium, and this unfavorable environment is transmitted to the progenitor cells responsible for replacing lost myocytes.
Progenitor cells become progressively less effective as the underlying pathologic process worsens and myocardial failure accelerates. These featuresnamely, the increased myocardial volume and mass, along with a net loss of myocytesare the hallmark of myocardial remodeling. This remodeling process leads to early adaptive mechanisms, such as augmentation of stroke volume and decreased wall stress and, later, to maladaptive mechanisms such as increased myocardial oxygen demand, myocardial ischemia, impaired contractility, and arrhythmogenesis.
As heart failure advances, there is a relative decline in the counterregulatory effects of endogenous vasodilators, including nitric oxide , prostaglandins , bradykinin , atrial natriuretic peptide , and B-type natriuretic peptide . This decline occurs simultaneously with the increase in vasoconstrictor substances from the RAAS and the adrenergic system, which fosters further increases in vasoconstriction and thus preload and afterload. This results in cellular proliferation, adverse myocardial remodeling, and antinatriuresis, with total body fluid excess and worsening of heart failure symptoms.
Also Check: What To Do In A Heart Attack
Treatment Of Comorbid Atrial Fibrillation And Cad
Atrial fibrillation is common in patients with HFpEF. The ACC/AHA and ESC guidelines recommend treatment of atrial fibrillation in these patients.3,5 Management includes identification and treatment of underlying causes , anticoagulation guided by appropriate risk stratification, and rate-control strategies using beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, and digoxin. No evidence supports a rhythm-control strategy unless rate control does not control symptoms.3,5 Complete revascularization is associated with improved mortality in patients with HFpEF and CAD who meet criteria for revascularization.3,30
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide And B

ANP and BNP are endogenously generated peptides activated in response to atrial and ventricular volume/pressure expansion. ANP and BNP are released from the atria and ventricles, respectively, and both promote vasodilation and natriuresis. Their hemodynamic effects are mediated by decreases in ventricular filling pressures, owing to reductions in cardiac preload and afterload. BNP, in particular, produces selective afferent arteriolar vasodilation and inhibits sodium reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule. It also inhibits renin and aldosterone release and, therefore, adrenergic activation. ANP and BNP are elevated in chronic heart failure. BNP especially has potentially important diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic implications.
For more information, see the Medscape Drugs & Diseases article Natriuretic Peptides in Congestive Heart Failure.
Don’t Miss: Symptoms Of Heart Failure Getting Worse
How Will I Find Out If I Have Heart Failure
Your doctor will diagnose heart failure based on your medical history, a physical exam, and test results. Bring a list of your symptoms to your appointment, including how often they happen and when they started. Also, bring a list of any prescription and over-the-counter medicines you take. Let your provider know if you have any risk factors for heart failure.
You may also be referred to a cardiologist for these tests and treatment. A cardiologist is a doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating heart diseases.
Lv Systolic Dysfunction In Hfpef
Along with diastolic dysfunction, it was shown that the symptoms of patients with HFpEF are related not only with LV diastolic dysfunction but also with an impaired LV longitudinal systolic function47,48 and impaired ventricular contractility.49,50 Moreover, other multiple non-diastolic abnormalities such as left atrial impairment, relative pericardial restraint, abnormal right ventricular-pulmonary artery coupling, pulmonary vascular disease, systemic vascular stiffening, coronary and peripheral microvascular dysfunction, and chronotropic incompetence are also contributed to the disease progression.51 A speckle-tracking analysis is a developing modality with additive value to standard echocardiography.52 LV global longitudinal strain is relatively independent of traditional diastolic parameters such as E/e and e18 and has confirmed that the longitudinal systolic function of the LV is significantly altered in a high proportion of patients with HFpEF.48 Moreover, impaired LV systolic mechanics in HFpEF also predict an increased risk of adverse outcomes.51,53,54
Don’t Miss: What Is The Pathway Of Blood Through The Heart
Defintions And Symptoms Of Heart Failure
These definitions of HF generally apply to the stages at which clinical symptoms are present and can be classified by either the New York Heart Association functional classification system or the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association classification which describes stages of HF based on structural changes and symptoms.2
Sometimes symptoms are nonspecific, making it unclear if there is heart failure or another medical condition.1 If HF is suspected, the first step in the diagnostic evaluation is a thorough clinical history and a physical exam. These results combined with blood tests will provide an indication of whether further testing is required. If all are normal, it may prompt the physician to look for other causes if an EKG is abnormal it may suggest moving on to other tests, such as an echocardiogram to further evaluate heart function.1
What Are The Types Of Heart Failure
There are many causes of heart failure, but the condition is generally broken down into these types:
Left-sided heart failure
Heart failure with reduced left ventricular function The lower left chamber of your heart gets bigger and cannot squeeze hard enough to pump the right amount of oxygen-rich blood to the rest of your body.
Heart failure with preserved left ventricular function Your heart contracts and pumps normally, but the bottom chambers of your heart are thicker and stiffer than normal. Because of this, your ventricles can’t relax properly and fill up all the way. Because there’s less blood in your ventricles, your heart pumps out less blood to the rest of your body when it contracts.
Right-sided heart failure
Heart failure can also affect the right side of your heart. Left-sided heart failure is the most common cause of this. Other causes include certain lung problems and issues in other organs.
Also Check: Does Coffee Raise Heart Rate
Diagnostic Criteria For Diastolic Heart Failure
A diagnosis of diastolic heart failure can be made if the patient exhibits clinical evidence of heart failure and has a normal left ventricular ejection fraction. The diagnosis is confirmed if there is evidence of ventricular hyperthrophy and/or concentric remodeling, left atrial enlargement, or laboratory evidence of diastolic dysfunction.
Holter Electrocardiography: Ambulatory Ecg And Long
-
Conventional Holter monitoring is of no value in the diagnosis of CHF, though it may detect and quantify the nature, frequency and duration of atrial and ventricular arrhythmias which could be causing or exacerbating symptoms of heart failure. Recording LTER should be restricted to patients with CHF and symptoms suggestive of an arrhythmia.
You May Like: How Do People Get Heart Attacks
Race Differences In Hfpef
So far, limited epidemiologic data are available regarding racial and ethnic differences in HFpEF. Data from the multiregional cross-sectional Identification of patients with heart failure and PREserved systolic Function: an Epidemiological Regional study demonstrated that HFpEF also accounts for a significant proportion of HF in non-Western countries.65 Interestingly, substantial regional variation with a higher incidence of HFpEF in Latin American and North Africa compared to the Middle East was observed.65,66 Compared to whites, African Americans have a 50% higher prevalence67 and ~80% higher incidence of HF.6870 Additionally, they have worse outcomes once HF develops regardless of LVEF.71,72 Besides, HFpEF accounts for up to 70% of prevalent HF in African Americans.66,73 A recent study from the Asian Sudden Cardiac Death in Heart Failure registry74 showed that Asian patients with HFpEF were relatively young and lean compared to those from Western populations, yet they carried a high comorbidity burden .74 Additionally, there were striking regional differences in types of comorbidities, cardiac remodelling and outcomes of HFpEF across Asia. These regional and ethnic differences should have important implications for public health measures and should be considered in the global HFpEF trial design.74
Framingham Heart Failure Diagnostic Criteria
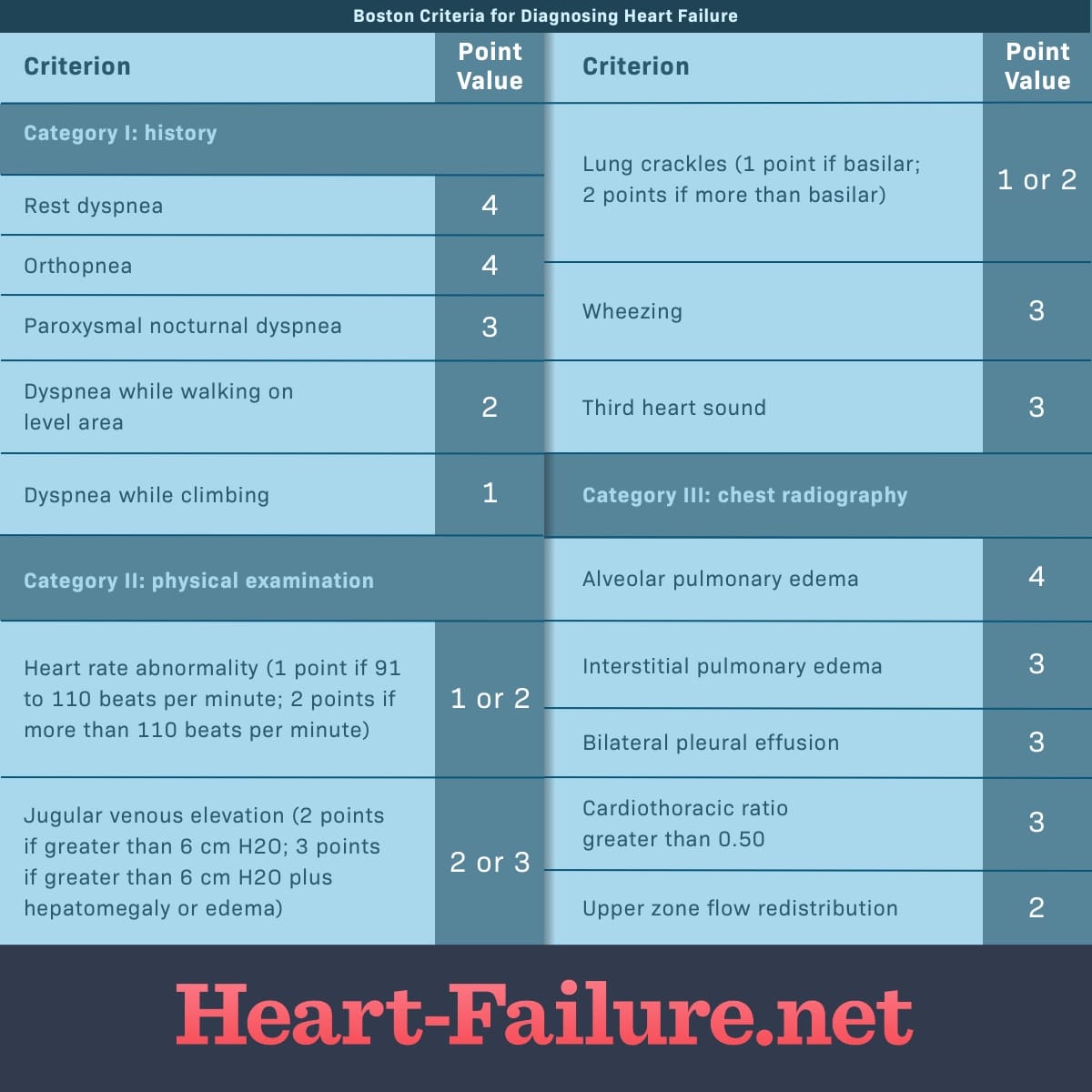
INSTRUCTIONS
Select minor criteria ONLY if they cannot be explained by another comorbidity, e.g. dyspnea on exertion secondary to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Patients with signs and symptoms of heart failure .
Minor criteria should only be selected if they cannot be explained by another comorbidity, e.g. dyspnea on exertion secondary to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
- Heart failure is a clinical diagnosis. The Framingham HF Diagnostic Criteria offer an acceptable set of criteria to make the diagnosis.
- Other diagnostic criteria include the New York Heart Association Classification.
2+ required for positive diagnosis
Also Check: What Information Would Be Included In The Care Plan Of An Infant In Heart Failure
Precipitating Causes Of Heart Failure
A previously stable, compensated patient may develop heart failure that is clinically apparent for the first time when the intrinsic process has advanced to a critical point, such as with further narrowing of a stenotic aortic valve or mitral valve. Alternatively, decompensation may occur as a result of the failure or exhaustion of the compensatory mechanisms but without any change in the load on the heart in patients with persistent, severe pressure or volume overload. In particular, consider whether the patient has underlying coronary artery disease or valvular heart disease.
The most common cause of decompensation in a previously compensated patient with heart failure is inappropriate reduction in the intensity of treatment, such as dietary sodium restriction, physical activity reduction, or drug regimen reduction. Uncontrolled hypertension is the second most common cause of decompensation, followed closely by cardiac arrhythmias . Arrhythmias, particularly ventricular arrhythmias, can be life threatening. Also, patients with one form of underlying heart disease that may be well compensated can develop heart failure when a second form of heart disease ensues. For example, a patient with chronic hypertension and asymptomatic LV hypertrophy may be asymptomatic until an MI develops and precipitates heart failure.
- Profound anemia
- Nutritional deficiencies
Heart Rhythm Society And The European Heart Rhythm Association Select Recommendations For Genetic Testing For Channelopathies And Cardiomyopathies
Long QT syndrome
Comprehensive or LQT1-3 targeted LQTS genetic testing is recommended for the following:
- Individuals with a strong clinical index of suspicion for LQTS based on the patient’s clinical history, family history, and expressed electrocardiographic phenotype
- Asymptomatic individuals with idiopathic QT prolongation on serial 12-lead ECGs defined as QTc over 480 ms or longer than 500 ms may also be considered in asymptomatic individuals with idiopathic QT prolongation on serial 12-lead ECGs for QTc values over 460 ms or longer than 480 ms
Mutation-specific genetic testing is recommended for family members following identification of the LQTS mutation in an index case.
Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
- Comprehensive or CPVT1 and CVPT2 targeted CPVT genetic testing is recommended for any individual with a clinical index of suspicion for CPVT based on the patient’s clinical history, family history, and expressed ECG phenotype during provocative stress testing with cycle, treadmill, or catecholamine infusion.
- Mutation-specific genetic testing is recommended for family members following identification of the CPVT mutation in an index case.
Brugada syndrome
Cardiac conduction disease
Short QT syndrome
ACM / arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy
Left ventricular noncompaction
Restrictive cardiomyopathy
Recommended Reading: How To Tell The Difference Between Heartburn And Heart Attack
