What Is A Heart Attack
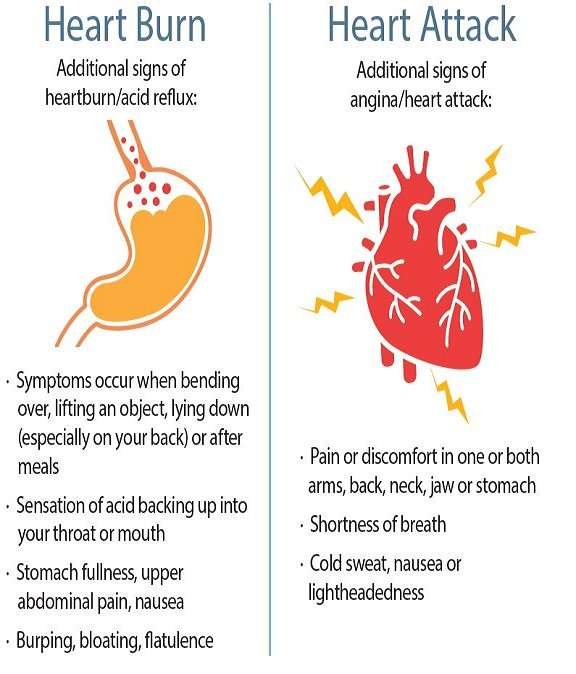
Heart attack signs and symptoms in men and women: Chest pain or discomfort Shortness of breath Pain or discomfort in the jaw, neck, back, arm, or shoulder Feeling nauseous, light-headed, or unusually tired.
A heart attack, also called a myocardial infarction, happens when a part of the heart muscle doesnt get enough blood.
The more time that passes without treatment to restore blood flow, the greater the damage to the heart muscle.
Coronary artery disease is the main cause of heart attack. A less common cause is a severe spasm, or sudden contraction, of a coronary artery that can stop blood flow to the heart muscle.
What Happens During A Heart Attack
When a heart attack happens, blood flow to a part of your heart stops or is far below normal, which causes that part of your heart muscle to die. When a part of your heart cant pump because its dying from lack of blood flow, it can disrupt the pumping sequence for the entire heart. That reduces or even stops blood flow to the rest of your body, which can be deadly if it isnt corrected quickly.
What Are The Symptoms Of Heart Attack
The major symptoms of a heart attack are
- Chest pain or discomfort. Most heart attacks involve discomfort in the center or left side of the chest that lasts for more than a few minutes or that goes away and comes back. The discomfort can feel like uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain.
- Feeling weak, light-headed, or faint. You may also break out into a cold sweat.
- Pain or discomfort in the jaw, neck, or back.
- Pain or discomfort in one or both arms or shoulders.
- Shortness of breath. This often comes along with chest discomfort, but shortness of breath also can happen before chest discomfort.
Other symptoms of a heart attack could include unusual or unexplained tiredness and nausea or vomiting. Women are more likely to have these other symptoms. Learn more about women and heart disease.
Every 40 seconds, someone in the United States has a heart attack.1Learn more facts about heart attack and heart disease.
You May Like: Heart Valve Replacement Surgery Recovery Elderly
Women And Heart Disease
Heart disease kills more than two times as many Australian women than breast cancer.
Moreover, about 40% of heart attacks in women are fatal, and many occur without prior warning. Sadly, the majority of women dont realise its one of their leading causes of death.
Why is heart disease less recognised in women?
- Women tend to develop symptoms of heart disease at a much later stage of the illness than men
- Their symptoms are often vaguer or non-specific
- Some diagnostic tests for heart disease are less accurate in women than in men
- Women are less likely to seek help quickly
- Some health professionals are less likely to check
Womens symptoms of a heart attack
Did you know that women can experience different symptoms of a heart attack to men and are often less likely to experience chest pain type symptoms?
If you arent feeling normal or are experiencing any of the symptoms above, head to your local emergency room or call 000. It is better to take care of yourself and prevent damage to your heart, in the event you are having a heart attack.
When does heart disease occur for women?
For earlier identification of cardiovascular disease and more timely and appropriate medical intervention it is advised for women over 45* to have a heart health check and to discuss their obstetric history if they have had children with their current GP. This enables proactive prevention to be taken to reduce risk. To learn more about risk factors for heart disease and how to reduce them .
Cause Of Most Heart Attacks Found
Researchers Say They May Know What Causes 90% of Heart Attacks
Aug. 30, 2004 — Heart researchers say nine risk factors — ones that you can do something about — account for 90% of all heart attacks.
Previously, researchers thought that only about half of heart attacks were explained by risk factors such as smoking or cholesterol. But now they say that the cause of almost all heart attacks can be pinpointed to one or more of the following:
- Eating too few fruits and vegetables
- Abstaining from alcohol
These risk factors are equal-opportunity killers — black or white, Asian or American, young or old, man or woman — all can fall victim by these same risks. Diet, exercise, and moderate consumption of alcohol can decrease risk of heart disease, but cannot reverse the potential danger posed by risks such as high cholesterol or smoking, says Salim Yusuf, MD, who led the study.
Studies have shown that men who drink up to two alcohol drinks a day and women who drink up to one a day have a lower risk of heart disease. One drink is generally considered to be four to five ounces of wine, a 12-ounce beer, or 1 ounce of liquor.
Read Also: Heart Attack Signs In Females
Research For Your Health
We are committed to advancing science and translating discoveries into clinical practice to promote the prevention and treatment of heart, lung, blood, and sleep disorders, including coronary heart disease. Learn about the current and future NHLBI efforts to improve health through research and scientific discovery. Research on this topic is part of the NHLBIs broader commitment to advancing scientific discovery for heart and vascular diseases.
How Common Is Heart Disease
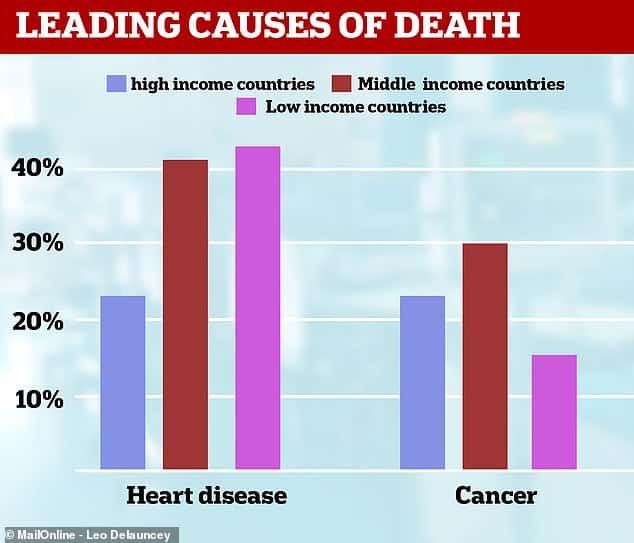
- Cardiovascular disease is the worlds leading cause of death. In 2019, 17.9 million people died from CVDs, comprising 32% of global mortality.
- Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the U.S. as well, causing approximately 697,000 deaths per year.
- Approximately 121.5 million U.S. adults have some form of cardiovascular disease.
Recommended Reading: Heart Rate Jumps When Standing
Are There Complications Of A Heart Attack
Complications following a heart attack can include:
- Arrhythmia your heart may develop an irregular heartbeat following a heart attack due to damaged heart muscles disrupting electrical signals.
- Heart failure your heart may have ongoing difficulty pumping enough blood, due to its muscles being too weak or stiff.
- Cardiogenic shock where your whole body goes into shock from extensive heart muscle damage.
- Heart rupture this is a rare but serious complication in which the hearts muscles, walls or valves split apart.
These can be dangerous if untreated, but your healthcare team will help to manage them if they occur.
What Are The Symptoms Of A Heart Attack
Heart attacks can have a number of symptoms, some of which are more common than others. The symptoms you have are also influenced by your sex, as with men and women being more likely to have different heart attack symptoms.
Common heart attack symptoms
Symptoms most often described by people having a heart attack:
- Chest pain . This symptom can be mild and feel like discomfort or heaviness, or it can be severe and feel like crushing pain. It may start in your chest and spread to other areas like your left arm , shoulder, neck, jaw, back or down toward your waist.
- Shortness of breath or trouble breathing.
- Nausea or stomach discomfort. Heart attacks can often be mistaken for indigestion.
- Heart palpitations.
- Feeling lightheaded, dizzy or passing out.
Heart attack symptoms in women
Medical research in recent years has shown that women may have the above symptoms, but also have a higher chance of experiencing symptoms different from those listed above.Women are less likely to describe the following:
- Chest pain, especially in the center of the chest.
- Discomfort that feels like indigestion.
Women are more likely to describe the following:
- Shortness of breath, fatigue and insomnia that started before the heart attack.
- Pain in the back, shoulders, neck, arms or abdomen.
- Nausea and vomiting.
Read Also: What Is A Dangerously High Heart Rate
Read Also: Lowering Resting Heart Rate
What Do I Do If I Have A Heart Attack
After a heart attack, you need quick treatment to open the blocked artery and lessen the damage. At the first signs of a heart attack, call 911. The best time to treat a heart attack is within 1 or 2 hours after symptoms begin. Waiting longer means more damage to your heart and a lower chance of survival.
If youâve called emergency services and are waiting for them to arrive, chew an aspirin . Aspirin is a potent inhibitor of blood clots and can lower the risk of death from a heart attack by 25%.
What Are The Warning Signs Of Heart Attack And Stroke
- pain or pressure in your chest that lasts longer than a few minutes or goes away and comes back
- pain or discomfort in one or both of your arms or shoulders, or your back, neck, or jaw
- shortness of breath
- indigestion or nausea
- feeling very tired
Treatment works best when it is given right away. Warning signs can be different in different people. You may not have all the listed symptoms.
Women may experience chest pain, nausea, and vomiting feel very tired and have pain that spreads to the back, neck, throat, arms, shoulders, or jaw. People with diabetes-related nerve damage may not notice any chest pain.
If you have angina, its important to know how and when to seek medical treatment.
- weakness or numbness of your face, arm, or leg on one side of your body
- confusion, or trouble talking or understanding
- dizziness, loss of balance, or trouble walking
- trouble seeing out of one or both eyes
- sudden, severe headache
If you have any one of these warning signs, call 9-1-1. You can help prevent permanent damage by getting to a hospital within an hour of a stroke.
Also Check: What Can You Do To Lower Your Heart Rate
What Does A Heart Attack Feel Like
Some of the sensations you may feel during a heart attack include:
- Chest pain that can range from mild to severe, or an uncomfortable pressure, tightness, squeezing or heaviness in your chest. The discomfort can last more than a few minutes at a time and sometimes goes away for a short time but returns later.
- Pain or a sensation of being squeezed that starts in the upper back.
- Pain that starts from your left shoulder and arm, and goes into other areas such as your back, jaw, neck or right arm.
- Pain that feels like heartburn or indigestion.
Many Other Heart Conditions Can Ultimately Lead To Heart Failure
All of us lose some blood-pumping ability in our hearts as we age, but heart failure results from the added stress of health conditions that either damage the heart or make it work too hard. All of the lifestyle factors that increase your risk of heart attack and stroke smoking, being overweight, eating foods high in fat and cholesterol and physical inactivity can also contribute to heart failure.
Learn more about what you can do to reduce your risk for heart failure by making lifestyle changes that last.
Don’t Miss: Women Having Heart Attacks
Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection
SCAD is a type of heart attack that happens when the inner lining of a coronary artery tears for no clear reason, slowing or blocking blood flow down the artery.
SCAD can occur in otherwise healthy people who do not have the typical risk factors of heart disease. And according to an article in Clinical Cardiology , about 90% of SCADs happen to women between the age of 30 and 60.
What To Do If You Think Someone Is Having A Heart Attack
Don’t Miss: Congestive Heart Disease
Risk Factors You Cant Control
- Age: The risk of heart disease increases for men after age 45 and for women after age 55 .
- Family history of early heart disease: You have a higher risk if your father or a brother was diagnosed with coronary artery disease before 55 years of age or if your mother or a sister was diagnosed with coronary artery disease before 65 years of age.
- Infections from bacteria and viruses
Watch our video on how SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, may affect your heart. Learn about how we support COVID-19 research.
Diabetes And Cardiovascular Disease Risk
People with diabetes are at greater risk of heart attack and stroke than people without diabetes.
The three main types of diabetes are:
- Type 1 diabetes where the body doesnt make insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes where the body becomes resistant to insulin.
- Gestational diabetes, which women can develop during pregnancy.
Insulin is the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels in the body.
Your doctor will check your blood sugar levels as part of a Heart Health Check. Depending on your overall risk of a heart attack or stroke, they may recommend you make changes to your diet and increase your physical activity. Some people with diabetes may also need to take medicines to manage their blood sugar levels.
Recommended Reading: What Is Heart Stent Surgery
You May Like: Why Do Av Nodal Cells Not Determine The Heart Rate
Major Risk Factors You Can Modify Treat Or Control
Tobacco smoke
The risk that smokers will develop coronary heart disease is much higher than that for nonsmokers.
Cigarette smoking is a powerful independent risk factor for sudden cardiac death in patients with coronary heart disease. Cigarette smoking also interacts with other risk factors to greatly increase the risk for coronary heart disease. Exposure to other peoples smoke increases the risk of heart disease even for nonsmokers.
Learn about smoking and cardiovascular disease
High blood cholesterol
As your blood cholesterol rises, so does your risk of coronary heart disease. When other risk factors are also present, this risk increases even more. A persons cholesterol level is also affected by age, sex, heredity and diet. Heres the lowdown on:
Learn more about managing your cholesterol.
High blood pressure
High blood pressure increases the hearts workload, causing the heart muscle to thicken and become stiffer. This stiffening of the heart muscle is not normal and causes the heart to function abnormally. It also increases your risk of stroke, heart attack, kidney failure and congestive heart failure.
When high blood pressure is present alongside obesity, smoking, high blood cholesterol levels or diabetes, the risk of heart attack or stroke increases even more.
Learn more about managing your blood pressure.
Physical inactivity
Learn more about getting active.
Obesity and being overweight
Learn more about managing your weight.
Diabetes
Do Women Fare Better Or Worse Than Men After A Heart Attack
Younger women under age 45 have a better outcome than men of a similar age. Scientists believe this is because of estrogen’s heart-protective effects. However, after menopause ends the protective benefits of estrogen, women fare worse than men. More specifically:
- Women between the ages of 45 and 65 who’ve had a heart attack are more likely to die within a year of the event compared with men of this same age.
- Women over age 65 are more likely to die within weeks of their heart attack than men over age 65.
Also Check: Why Is My Heart Rate Variability So Low
Treatment For A Heart Attack
The goal of treatment for a heart attack is to relieve pain, preserve the heart muscle function, and prevent death.
Treatment in the emergency department may include:
- Intravenous therapy, such as nitroglycerin and morphine
- Continuous monitoring of the heart and vital signs
- Oxygen therapy to improve oxygenation to the damaged heart muscle
- Pain medicine to decrease pain. This, in turn, decreases the workload of the heart. The oxygen demand of the heart decreases.
- Cardiac medicine such as beta-blockers to promote blood flow to the heart, improve the blood supply, prevent arrhythmias, and decrease heart rate and blood pressure
- Fibrinolytic therapy. This is the intravenous infusion of a medicine that dissolves the blood clot, restoring blood flow.
- Antithrombin or antiplatelet therapy with aspirin or clopidogrel. This is used to prevent further blood clotting.
- Antihyperlipidemics. These medicines lower lipids in the blood, particularly low density lipid cholesterol. Statins are a group of antihyperlipidemic medicines. They include simvastatin, atorvastatin, and pravastatin. Bile acid sequestrantscolesevelam, cholestyramine, and colestipoland nicotinic acid are two other types of medicines that may be used to lower cholesterol levels.
You may need other procedures to restore blood flow to the heart. Those procedures are described below.
Overweight/obesity And Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Being overweight or obese increases the risk of having a heart attack and stroke, along with other health problems including:
- sleep problems, such as sleep apnoea
- certain types of cancer.
Carrying extra weight around your tummy is also a risk factor for heart disease. Speak to your health professional for support to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Recommended Reading: Silent Heart Attacks In Women
