Myocytes And Myocardial Remodeling
In the failing heart, increased myocardial volume is characterized by larger myocytes approaching the end of their life cycle. As more myocytes drop out, an increased load is placed on the remaining myocardium, and this unfavorable environment is transmitted to the progenitor cells responsible for replacing lost myocytes.
Progenitor cells become progressively less effective as the underlying pathologic process worsens and myocardial failure accelerates. These featuresnamely, the increased myocardial volume and mass, along with a net loss of myocytesare the hallmark of myocardial remodeling. This remodeling process leads to early adaptive mechanisms, such as augmentation of stroke volume and decreased wall stress and, later, to maladaptive mechanisms such as increased myocardial oxygen demand, myocardial ischemia, impaired contractility, and arrhythmogenesis.
As heart failure advances, there is a relative decline in the counterregulatory effects of endogenous vasodilators, including nitric oxide , prostaglandins , bradykinin , atrial natriuretic peptide , and B-type natriuretic peptide . This decline occurs simultaneously with the increase in vasoconstrictor substances from the RAAS and the adrenergic system, which fosters further increases in vasoconstriction and thus preload and afterload. This results in cellular proliferation, adverse myocardial remodeling, and antinatriuresis, with total body fluid excess and worsening of heart failure symptoms.
Common Signs And Symptoms Of Heart Failure
It is very important for you to manage your other health conditions, such as diabetes, kidney disease, anemia, high blood pressure, thyroid disease and asthma or chronic lung disease. Some conditions have signs and symptoms that are similar to heart failure. If you have new or worsening non-urgent symptoms, tell your healthcare provider.
Dont Miss: What Heart Chamber Pushes Blood Through The Aortic Semilunar Valve
Medical History And Physical Exam
Bring a list of your symptoms to your doctors appointment, including how often they happen and when they started. Also, bring a list of any prescription and over-the-counter medicines you take. Let your doctor know if you have any risk factors for heart failure.
During your physical exam, your doctor will:
- Measure your heart rate, blood pressure, and body weight.
- Listen to your heart with a stethoscope for sounds that suggest that your heart is not working properly.
- Listen to your lungs for the sounds of fluid buildup.
- Look for swelling in your ankles, feet, legs, liver, and veins in your neck.
You May Like: How Does Advil Cause Heart Attacks
Precipitating Causes Of Heart Failure
A previously stable, compensated patient may develop heart failure that is clinically apparent for the first time when the intrinsic process has advanced to a critical point, such as with further narrowing of a stenotic aortic valve or mitral valve. Alternatively, decompensation may occur as a result of the failure or exhaustion of the compensatory mechanisms but without any change in the load on the heart in patients with persistent, severe pressure or volume overload. In particular, consider whether the patient has underlying coronary artery disease or valvular heart disease.
The most common cause of decompensation in a previously compensated patient with heart failure is inappropriate reduction in the intensity of treatment, such as dietary sodium restriction, physical activity reduction, or drug regimen reduction. Uncontrolled hypertension is the second most common cause of decompensation, followed closely by cardiac arrhythmias . Arrhythmias, particularly ventricular arrhythmias, can be life threatening. Also, patients with one form of underlying heart disease that may be well compensated can develop heart failure when a second form of heart disease ensues. For example, a patient with chronic hypertension and asymptomatic LV hypertrophy may be asymptomatic until an MI develops and precipitates heart failure.
- Profound anemia
- Nutritional deficiencies
Patient Discussion About Congestive Heart Failure
Q. What Is the Treatment for Congestive Heart Failure? My mother is 76 years ols and has been suffering from a heart disease for many years. Lately she has developed congestive heart failure. How is this situation treated?
A.
Q. congestive heart failure how it works is it to do with fluid built up in your body
A.
Q. describe the symptoms of congestive heart failure
A.
Read Also: When Checking Your Pulse During Exercise, You Should Measure Your Heart Rate For 30 Seconds.
What Are The Types Of Heart Failure
There are many causes of heart failure, but the condition is generally broken down into these types:
Left-sided heart failure
Heart failure with reduced left ventricular function The lower left chamber of your heart gets bigger and cannot squeeze hard enough to pump the right amount of oxygen-rich blood to the rest of your body.
Heart failure with preserved left ventricular function Your heart contracts and pumps normally, but the bottom chambers of your heart are thicker and stiffer than normal. Because of this, your ventricles can’t relax properly and fill up all the way. Because there’s less blood in your ventricles, your heart pumps out less blood to the rest of your body when it contracts.
Right-sided heart failure
Heart failure can also affect the right side of your heart. Left-sided heart failure is the most common cause of this. Other causes include certain lung problems and issues in other organs.
What Are The Symptoms Of Heart Failure
You may not have any symptoms of heart failure, or the symptoms may be mild to severe. Symptoms can be constant or can come and go. The symptoms can include:
- Congested lungs. Fluid backup in the lungs can cause shortness of breath with exercise or difficulty breathing at rest or when lying flat in bed. Lung congestion can also cause a dry, hacking cough or wheezing.
- Fluid and water retention. Less blood to your kidneys causes fluid and water retention, resulting in swollen ankles, legs, abdomen , and weight gain. Symptoms may cause an increased need to urinate during the night. Bloating in your stomach may cause a loss of appetite or nausea.
- Dizziness, fatigue, and weakness. Less blood to your major organs and muscles makes you feel tired and weak. Less blood to the brain can cause dizziness or confusion.
- Rapid or irregular heartbeats. The heart beats faster to pump enough blood to the body. This can cause a rapid or irregular heartbeat.
If you have heart failure, you may have one or all of these symptoms or you may have none of them. They may or may not indicate a weakened heart.
Don’t Miss: What Should Your Heart Rate Be When Exercising
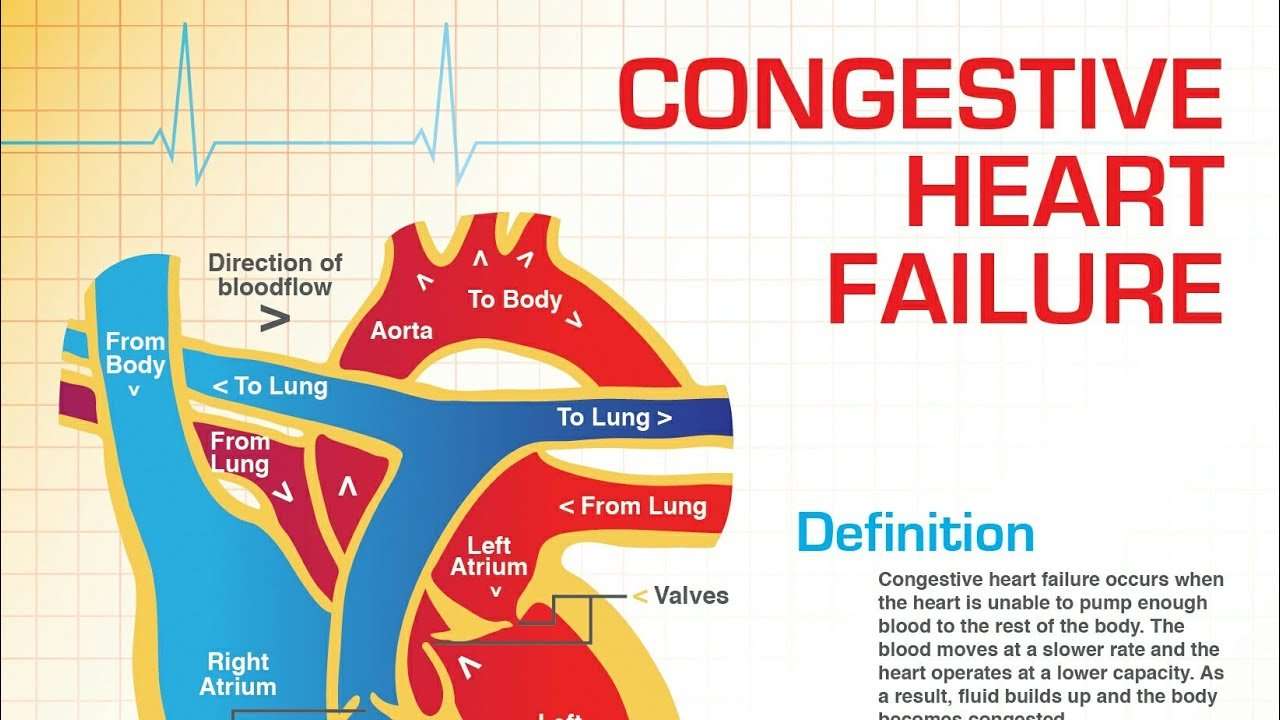
About Congestive Heart Failure
Heart failure, sometimes called congestive cardiac failure , is a condition in which the heart muscle is weakened and cant pump as well as it usually does. The main pumping chambers of the heart can change size and thickness, and either cant contract or cant relax as well as they should. This triggers fluid retention, particularly in the lungs, legs and abdomen.
The major causes of heart failure include coronary heart disease and heart attack, high blood pressure, damage to the heart muscle , heart valve problems and abnormal heart rhythms. Of these, coronary heart disease and heart attack are the most common causes.
The major factors that contribute to coronary heart disease include:
- reduced emotional and social wellbeing
- physical inactivity.
Heart failure is more common in elderly people. The survival rate for people with this disorder depends on the severity of their condition.
Most common treatments for heart failure are medications and self-managed lifestyle changes. Some less-common treatments may require insertion of implantable cardiac devices or valve replacement.
You May Like: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
What Is The Outlook With Heart Failure
With the right care, congestive heart failure wont stop you from doing the things you enjoy. Your prognosis, or outlook for the future, will depend on:
- How well your heart muscle is working.
- Your symptoms.
- How well you respond to your treatment plan.
- How well you follow your treatment plan.
One study says that people with heart failure have a life span 10 years shorter than those who dont have heart failure. Another study showed that the survival rates of people with chronic heart failure were 80% to 90% for one year, but that dropped to 50% to 60% for year five and down to 30% for 10 years.
A different study found that people who had heart failure and were discharged from the hospital had expected life spans ranging from three to 20 years, depending on various factors like age and gender. Its important to look at your specific situation when considering your prognosis.
Read Also: Why Do I Have Heart Palpitations
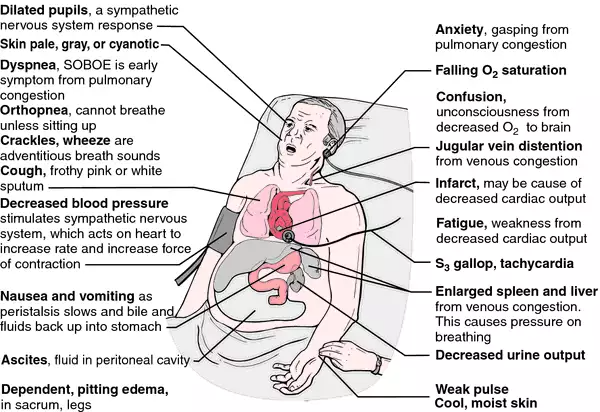
Congestive Heart Failure Symptoms
Signs of heart failure can appear in anyone at any age, even in young children that may be born with heart defects. But it usually affects older people with weakened hearts from other diseases.
There may be no symptoms in the early stages, but people start having symptoms in stage II and they get progressively worse, especially without treatment.
Symptoms include:
- Feelings of anxiety, suffocation and restlessness
- Hacking, dry cough that happens more often when lying down
- Having to urinate more often at night
- Lung congestion and difficulty breathing from blood backing up into the lungs
- Nausea, abdominal swelling, tenderness or pain
- Swelling from fluid buildup, especially in the feet, ankles and legs
- Weight gain from fluid buildup or weight loss from poor nutrient absorption and decreased appetite
Treatments For Heart Failure
Treatment for heart failure usually aims to control the symptoms for as long as possible and slow down the progression of the condition.
How you’re treated will depend on what is causing your heart failure.
Common treatments include:
- lifestyle changes including eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly and stopping smoking
- medicine a range of medicines can help many people need to take 2 or 3 different types
- devices implanted in your chest these can help control your heart rhythm
- surgery such as a or a heart transplant
Treatment will usually be needed for life.
A cure may be possible when heart failure has a treatable cause. For example, if your heart valves are damaged, replacing or repairing them may cure the condition.
Also Check: Symptoms Right Sided Heart Failure
Heart Failure Treatment Is A Team Effort
Heart failure management is a team effort, and you are the key player on the team. Your heart doctor will prescribe your medications and manage other medical problems. Other team members — including nurses, dietitians, pharmacists, exercise specialists, and social workers — will help you achieve success. But it is up to YOU to take your medications, make dietary changes, live a healthy lifestyle, keep your follow-up appointments, and be an active member of the team.
If you notice anything unusual, don’t wait until your next appointment to discuss it with your doctor. Call them right away if you have:
- Unexplained weight gain
- Swelling in your ankles, feet, legs, or belly that gets worse
- Shortness of breath that gets worse or happens more often, especially if you wake up feeling that way
- Bloating with a loss of appetite or nausea
- Extreme fatigue or more trouble finishing your daily activities
- A lung infection or a cough that gets worse
- Fast heart rate
- New irregular heartbeat
Is There A Treatment For Heart Failure
There are more treatment options available for heart failure than ever before. Tight control over your medications and lifestyle, coupled with careful monitoring, are the first steps. As the condition progresses, doctors specializing in the treatment of heart failure can offer more advanced treatment options.
The goals of treating heart failure are to try to keep it from getting worse , to ease symptoms, and to improve quality of life.
Some common types of medicines used to treat it are:
- ACE inhibitors
- Aldosterone antagonists
- Selective sinus node inhibitors
- Soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator
Your doctor may also recommend a program called cardiac rehabilitation to help you exercise safely and keep up a heart-healthy lifestyle. It usually includes workouts that are designed just for you, education, and tips to lower your chance of heart trouble, like quitting smoking or changing your diet.
Cardiac rehab also offers emotional support. You can meet people like you who can help you stay on track.
You May Like: What Are The Different Types Of Heart Surgery
Causes Of Heart Failure
Heart failure is often the result of a number of problems affecting the heart at the same time.
Conditions that can lead to heart failure include:
- coronary heart disease where the arteries that supply blood to the heart become clogged up with fatty substances , which may cause angina or a heart attack
- high blood pressure this can put extra strain on the heart, which over time can lead to heart failure
- conditions affecting the heart muscle
- heart rhythm problems , such as atrial fibrillation
- damage or other problems with the heart valves
- congenital heart disease birth defects that affect the normal workings of the heart
Sometimes obesity, anaemia, drinking too much alcohol, an overactive thyroid or high pressure in the lungs can also lead to heart failure.
When Should I Get Emergency Care
Go to the ER or call 911 if you have:
- New, unexplained, and severe chest pain that comes with shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, or weakness
- Fast heart rate , especially if you are short of breath
- Shortness of breath that doesn’t get better if you rest
- Sudden weakness, or you can’t move your arms or legs
- Sudden, severe headache
- Fainting spells
Recommended Reading: Is Blood Pressure Related To Heart Rate
Medical Definition Of Congestive Heart Failure
- Medical Editor: Jay W. Marks, MD
Reviewed on 6/3/2021
Congestive heart failure: Inability of the heart to keep up with the demands on it, with failure of the heart to pump blood with normal efficiency. When this occurs, the heart is unable to provide adequate blood flow to other organs, such as the brain, liver, and kidneys. Abbreviated CHF. CHF may be due to failure of the right or left ventricle, or both. The symptoms can include shortness of breath , asthma due to the heart , pooling of blood in the general body circulation or in the livers circulation, swelling , blueness or duskiness , and enlargement of the heart. The many causes of CHF include coronary artery disease leading to heart attacks and heart muscle weakness primary heart muscle weakness from viral infections or toxins, such as prolonged alcohol exposure heart valve disease causing heart muscle weakness due to too much leaking of blood or causing heart muscle stiffness from a blocked valve hyperthyroidism and high blood pressure.
Can Surgery Be Used To Treat Heart Failure
In heart failure, surgery may sometimes prevent further damage to the heart and improve the heart’s function. Procedures used include:
- Coronary artery bypass grafting surgery. The most common surgery for heart failure caused by coronary artery disease is . Although surgery is more risky for people with heart failure, new strategies before, during, and after surgery have reduced the risks and improved outcomes.
- Heart valve surgery. Diseased heart valves can be treated both surgically and non-surgically .
- Implantable left ventricular assist device . The LVAD is known as the “bridge to transplantation” for patients who haven’t responded to other treatments and are hospitalized with severe systolic heart failure. This device helps your heart pump blood throughout your body. It allows you to be mobile, sometimes returning home to await a heart transplant. It may also be used as destination therapy for long-term support in patients who are not eligible for transplant.
- Heart transplant. A heart transplant is considered when heart failure is so severe that it doesn’t respond to all other therapies, but the person’s health is otherwise good.
Recommended Reading: How Blood Moves Through The Heart
What Medications Should I Avoid If I Have Heart Failure
There are several different types of medications that are best avoided in those with heart failure including:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications such as Motrin or Aleve. For relief of aches, pains, or fever take Tylenol instead.
- Most calcium channel blockers
- Some nutritional supplements, such as salt substitutes, and growth hormone therapies
- Antacids that contain sodium
If youâre taking any of these drugs, discuss them with your doctor.
Itâs important to know the names of your medications, what theyâre used for, and how often and at what times you take them. Keep a list of your medications and bring them with you to each of your doctor visits. Never stop taking your medications without discussing it with your doctor. Even if you have no symptoms, your medications decrease the work of your heart so that it can pump more effectively.
Drugwatchcom Has Been Empowering Patients For More Than A Decade
Drugwatch.com has provided reliable, trusted information about medications, medical devices and general health since 2008. Weve also connected thousands of people injured by drugs and medical devices with top-ranked national law firms to take action against negligent corporations.
Our team includes experienced medical writers, award-winning journalists, researchers and certified medical and legal experts. Drugwatch.com is HONCode certified. This means the high-quality information we provide comes from credible sources, such as peer-reviewed medical journals and expert interviews.
The information on Drugwatch.com has been medically and legally reviewed by more than 30 expert contributors, including doctors, pharmacists, lawyers, patient advocates and other health care professionals. Our writers are members of professional associations, including American Medical Writers Association, American Bar Association, The Alliance of Professional Health Advocates and International Society for Medical Publication Professionals.
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms For Congestive Heart Failure
What Are The 4 Stages Of Congestive Heart Failure
Years ago, the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology identified the stages of congestive heart failure. Those stages were updated and revised in 2005. Understanding these stages can help you recognize that congestive heart failure is a progressive disease that can worsen over time.
Here is a description of the 4 Stages of Congestive Heart Failure:
