Why Is This A Problem
Srivatsa: AFib is a common reason for emergency department visits and hospitalizations. Its also a significant cause of heart failure and disabling strokes that occur when clots form in pooled blood in the left atrium and travel to the head.
AFib occurs when the right and left atria beat out-of-sync, reducing the hearts ability to pump efficiently.
Understanding Afib: How To Measure Your Own Heart Rate And Rhythm
George, the patient we have been following through the Understanding AFib series, found it easy to recognize when his heart was in atrial fibrillation and beating very quickly . Like a heart dancing without rhythm, the rapid, irregular heart rate made him unable to exert himself.
Once George started the beta blocker, metoprolol, to slow down his heart, he felt better. But it became more difficult for him to tell whether his heart was in a normal pattern of beating or in AFib.
His doctor ordered a three-day, continuous electrocardiogram monitor that confirmed he was in AFib several times for an hour at a time. He would have benefited from knowing when he was in AFib earlier, without having to wait for the test results.
In previous posts, we discussed blood thinning medications that reduce the chances of stroke and medications used to slow down the heart. But as you might guess, drugs are only part of the strategy to remain healthy with AFib.
Several other important, heart-healthy strategies, include:
- Avoid stimulants, including excessive caffeine, that can speed up the heart.
- Take your heart-rate control medications consistently. Heart rates can speed up very quickly when beta blockers are stopped abruptly.
- Limit alcohol consumption. It is generally safe for women to have one drink per day and for men to have two.
You can tell you are in AFib by paying close attention to whether your heartbeat is regular or irregular:
To measure your heart rate:
How Are Heart Attack Symptoms Different From Afib Symptoms
Fluttering and palpitations are key symptoms of AFib and is the key difference, but many heart problems have similar warning signs. If you think you may be having a heart attack, DONT DELAY. Get emergency help by calling 911 immediately. A heart attack is a blockage of blood flow to the heart, often caused by a clot or build-up of plaque lodging in the coronary artery . A heart attack can damage or destroy part of your heart muscle. Some heart attacks are sudden and intense where no one doubts what’s happening. But most heart attacks start slowly, with mild pain or discomfort. Often people affected aren’t sure what’s wrong and wait too long before getting help.
Also Check: How Do You Know If You Are Having A Heart Attack
How Is Afib With Rvr Treated
Short-term treatment depends on your overall condition. If you arenât stable, youâll probably get:
- Drugs called beta-blockers. They control your heart rate. Your doctor will get them to you in your vein if you have AFib with RVR. The most commonly used drugs are:
Your doctorâs goal is to get you stable enough for:
- Electrical cardioversion: Your doctor gives your heart a shock to reset your heartbeat. Theyâll use paddles or stick patches called electrodes onto your chest.
- First, you’ll get medicine to make you fall asleep. Then, your doctor will put the paddles on your chest, and sometimes your back. These will give you a mild electrical shock to get your heart’s rhythm back to normal.
- Most people only need one. Because youâre sedated, you probably wonât remember being shocked. You can usually go home the same day.
- Your skin may be irritated where the paddles touched it. Your doctor can recommend a lotion to ease pain or itching.
If youâre more stable, youâll just get heart rate medications and you and the doctor can decide if you need cardioversion later.
Once your heart rate is under control, they may suggest long-term treatment with a wider choice of beta-blockers:
Does Bradycardia Require Treatment
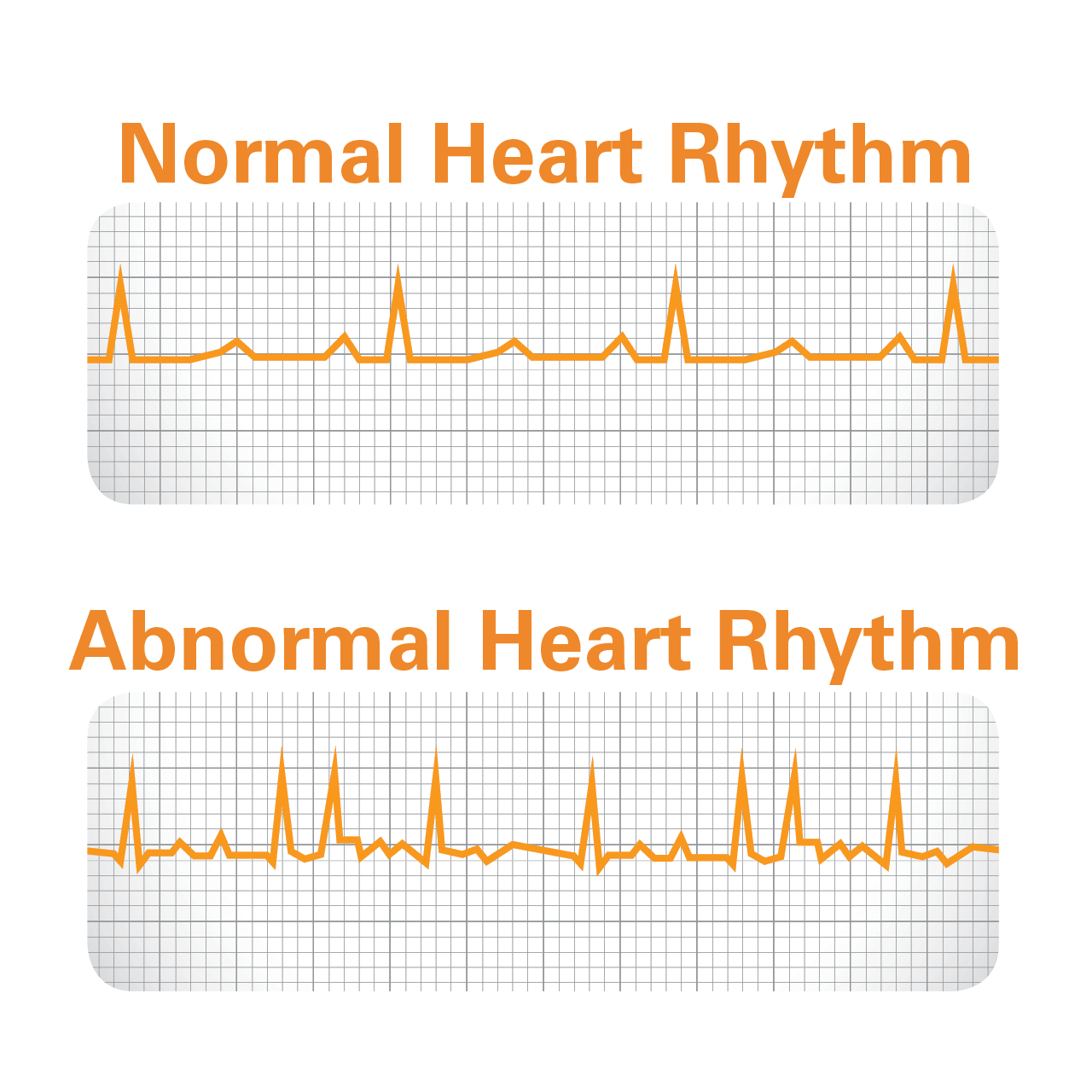
If your heart rate is slow, but you dont have symptoms, theres no reason to worry. However, its a good idea to know the signs of trouble because bradycardia in some cases does require treatment.
For example, if your heart rate drops into the 30s, you might not get enough oxygen to your brain, making fainting, lightheadedness, and shortness of breath possible. Blood can also pool in your heart chambers, causing congestive heart failure.
Also Check: What Does Heart Rate Mean
Types Of Atrial Fibrillation
AFib doesnât so much have types as it has durations. Doctors classify it by how long it lasts, or what causes it. Yours could change over time. Your treatment will depend on which you have.
Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. This is an episode of atrial fibrillation that lasts less than a week. You might feel it happening for a few minutes or for several days. You may not need treatment with this type of AFib, but you should see a doctor.
You could hear it nicknamed âholiday heart syndrome.â This refers to AFib that follows a bout of heavy drinking. If your heart isnât used to all this different activity, it may go into AFib. It also happens sometimes when youâre under extreme stress.
Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. Persistent AFib usually starts as short-term AFib . Usually, this lasts longer than a week. Youâre more likely to get persistent AFib if youâre:
- Have high blood pressure, heart failure, coronary heart disease, chronic pulmonary obstructive disease , or heart valve disease
- A former smoker
It could stop on its own, or you may need medicine or treatment to stop it. Doctors can use medicine to treat this type of AFib. If that doesnât work, they might use a low-voltage current to reset your heartâs rhythm to normal. Itâs called electrical cardioversion. Doctors usually do this procedure in a hospital while youâre sedated, so you wonât feel anything. You can go home after itâs done, but someone else will have to drive you.
- Have sleep apnea
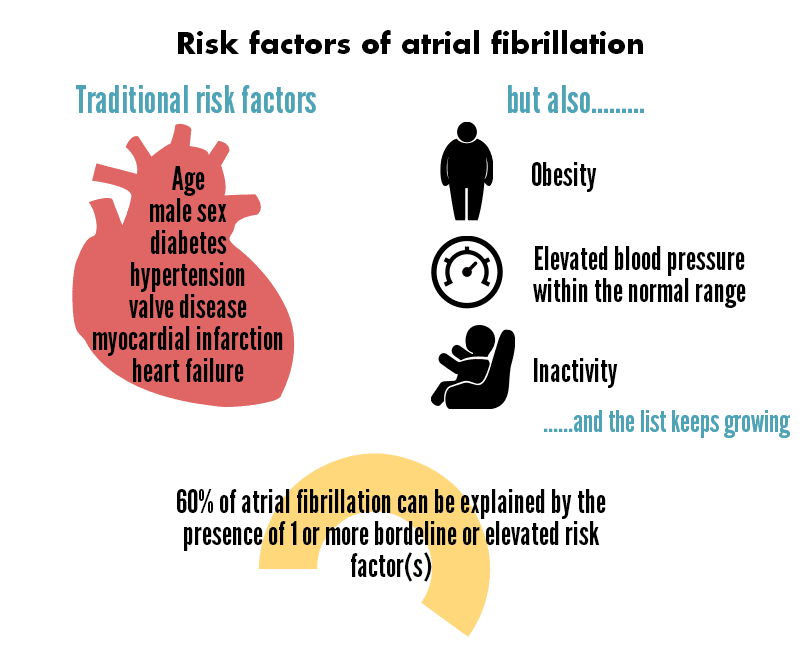
Why Does Atrial Fibrillation Happen And How Common Is It
Atrial fibrillation is the most common heart rhythm disturbance and affects up to 800,000 people in the UK.
The cause of atrial fibrillation is not fully understood, but it tends to occur in certain groups of people and may be triggered by certain situations, such as drinking excessive amounts of alcohol or smoking.
The condition can affect adults of any age or gender but:
- is more common the older you get
- affects about 10% of people over 75
- more common in men than women
Atrial fibrillation is more likely to occur in people with other conditions, such as:
- high blood pressure
Find out more abou the causes of atrial fibrillation and how it’s diagnosed
Recommended Reading: How Do You Find Your Maximum Heart Rate
Categories Of Atrial Fibrillation
Your atrial fibrillation will fall into one of several categories. This classification system is spelled out in the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation that is used by cardiologists, electrophysiologists, and surgeons.
- Paroxysmal, or intermittent episodes that come and go and last seven days or less
- Persistent continuous atrial fibrillation that lasts more than seven days
- Longstanding persistent continuous afib that lasts longer than one year
- Permanent continuous atrial fibrillation in which a decision has been made by the patient and the doctor not to try to restore normal sinus rhythm by any means, including catheter or surgical ablation
Afib is progressive. Afib begets afib. You may start out with intermittent or paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and over time migrate to persistent atrial fibrillation. Or you may start out with persistent afib and migrate to longstanding persistent afib, or even permanent afib.
For purposes of discussing treatment here, we will discuss only paroxysmal, persistent and longstanding persistent atrial fibrillation. There are so many options now for atrial fibrillation treatment that the decision to not treat, and thus to be in permanent atrial fibrillation, is becoming increasingly rare. Some doctors now consider permanent afib to be an obsolete category.
Recommended Reading: Is 190 Heart Rate Bad
What Are The Symptoms Of Atrial Fibrillation
You might be wondering what Afib feels like. Some people with Afib have no symptoms. It depends on how fast your ventricles are beating. If theyre beating at a normal or slightly elevated pace, you probably wont feel anything. But if your ventricles beat faster then youll start to notice symptoms. These can include:
If you have symptoms, keep a list of when they happen and share this information with your healthcare provider right away.
Don’t Miss: Quadruple Heart Bypass Surgery
Pearls And Other Issues
Atrial fibrillation is a commonly encountered disease that affects many individuals. Advancing age is associated with increased prevalence, with the most catastrophic complication being an acute hemorrhagic stroke. Due to the irregularity of the atria, blood flow through this chamber becomes turbulent, leading to thrombus formation. The most common site for this embolus is the atrial appendage. The thrombus can dislodge and embolize to the brain and other parts of the body. It is essential for the patient to seek medical care immediately if they are experiencing chest pain, palpitations, shortness of breath, severe sweating, or extreme dizziness.
Next Steps And Considerations
Treating atrial fibrillation aims to reduce the risk of stroke due to thromboembolism and to control the ventricular heart rate. Restoring the patients cardiac rhythm to a sinus rhythm may or may not be a goal for all patients. Endpoints of the Adult Tachycardia with a Pulse Algorithm recommend the patient with atrial fibrillation who underwent synchronized cardioversion consult with experts for further evaluation and treatment. If the patient with atrial fibrillation is considered stable but has been experiencing atrial fibrillation for more than 48 hours, cardioversion should be delayed until the patient has been properly anticoagulated to reduce the risk of thromboembolism and stroke. Cardioversion for the patient with stable atrial fibrillation would then be conducted under the care of an expert.
Recommended Reading: How To Know If You’re Having A Heart Attack
How Can I Check For Afib At Home
If you think you have Afib symptoms, its important to call your healthcare provider right away to discuss how youre feeling. Your provider may ask you to check your pulse. If it feels erratic or weak, that could be a sign youre in Afib.However, sometimes you might not notice any changes in your pulse, especially if your Afib isnt advanced. You may instead just feel tired or out of breath. You may not know if your symptoms are from Afib or something else. Thats why a call to your provider is essential.
How Is Atrial Fibrillation Diagnosed
To diagnose atrial fibrillation, your healthcare provider will first ask you some questions. Youll share information about your diet and physical activity, family history, any symptoms youve noticed and risk factors. Its OK if you dont know all the answers but share as much as you can. Your experiences and knowledge are essential tools to help your provider make a diagnosis. Your provider will then give you a physical exam that includes:
- Listening to your heart rhythm with a stethoscope.
- Checking your pulse and blood pressure.
- Checking the size of your thyroid gland to identify thyroid problems.
- Looking for swelling in your feet or legs to identify heart failure.
- Listening to your lungs to detect heart failure or infection.
This exam will help your provider understand your baseline health and how your body is functioning.
Tests to diagnose atrial fibrillation
In addition to the physical exam, your provider may run some tests to make an atrial fibrillation diagnosis. These tests include:
In some cases, your provider may want to check how your heart works in your daily life. If so, youll be asked to wear a Holter monitor or a portable event monitor to record your hearts activity.
An EKG records your hearts electrical impulses and can show if you have atrial fibrillation.
Don’t Miss: What Does A Heart Attack Look Like
How Is Atrial Fibrillation Defined
Atrial fibrillation is defined in various ways, depending on how it affects you:
- paroxysmal atrial fibrillation – this comes and goes, usually stopping within 48 hours without any treatment.
- persistent atrial fibrillation – this lasts for longer than seven days, or less when it is treated.
- longstanding persistent atrial fibrillation – this means you have had continuous atrial fibrillation for a year or longer.
- permanent atrial fibrillation – this is when atrial fibrillation is present all the time and no more attempts to restore normal heart rhythm will be made
Screening For Atrial Fibrillation
To screen for AF, your doctor may take your medical history and do some tests, such as:
- a physical exam and checking your pulse
- blood tests to rule out other causes
- taking an electrocardiogram , the main tool for diagnosing AF which measures the hearts electrical activity
- taking an echocardiogram, an ultrasound that produces moving pictures of the heart that can help show structural heart disease or blood clots in the heart.
As AF symptoms are intermittent, the use of a portable ECG device may be needed. Handheld ECGs and smartwatches with ECGs are increasingly available to consumers.
Medical devices can be worn by patients to record the electrical activity of their heart for longer periods of time, increasing the chance that the AF symptoms will be recorded. A Holter monitor can be used to record the hearts activity for 24 hours or longer, while patches can record for two weeks. An event recorder can be used to record the hearts activity over weeks to months.
While only your doctor can diagnose AF, you can keep an eye on your heart health by regularly checking your pulse.
You May Like: What Effect Do Natriuretic Peptides Have During Heart Failure When The Heart Dilates
Will Atrial Fibrillation Make My Life Harder
You might find it harder when getting used to a new routine. AF is a manageable condition and with the right treatment you can carry on as you were before you were diagnosed.
Talking to people about your condition can be hard. Dealing with stress and anxiety is also common after being told you have a heart condition. Visit our emotional support hub for advice and support if youre struggling with the change of pace.
You might have to think about practical matters, like driving, going on holiday or travel insurance after being diagnosed with AF. Again, your GP can help with any queries you might have.
Can It Be Prevented
Srivatsa: Like most heart disease, AFib is often preventable with healthy lifestyle practices. Limiting alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, eating a heart-healthy diet and exercising every day, and regular meditation have been shown to reduce the likelihood of AFib or help alleviate symptoms once it is diagnosed.
Recommended Reading: Signs Of Congested Heart Failure
Diagnosing Afib With Rvr
The only way to definitively diagnose AFib, as well as RVR, is to get an electrocardiogram . This is a diagnostic tool that records the electrical activity of your heart. AFib and RVR create distinctive patterns of electrical waves on an EKG that doctors can use to confirm the presence of the arrhythmia.
An EKG can be performed in a doctors office, but a 24-hour recording of the heart can also be made using a Holter monitor. This gives a more complete picture of what the heart is doing. Heart monitors may be worn for more extended periods as well.
Expert Care For This Common Type Of Irregular Heartbeat
Atrial fibrillation, or AFib, is the most common type of arrhythmia , in which the hearts two upper chambers do not beat in sync with the two lower chambers. Our patients sometimes describe it as feeling like theres a fish jumping in my chest.
A normal heart rate for adults ranges from 60 to 100 beats a minute. If you have atrial fibrillation, your heart may beat much faster, up to 100 to 175 times a minute, or much slower.
Although AFib by itself is not life-threatening, it can increase your risk of stroke and heart failure if not treated. In fact, it causes about 20 percent of all strokes because blood pools in the heart chambers and clots form.
AFib is the most common type of arrhythmia, affecting more than 5 million people in the U.S.a figure that keeps growing as the population ages. Our Cardiac Electrophysiology Program is a national leader in performing ablation procedures, such as cryoablation procedures, for AFib management. We also have the mid-Atlantics most experienced facility using the WATCHMAN device, which can prevent blood clots from forming and causing strokes in patients.
Read Also: How Long Do Heart Palpitations Last
Read Also: Does Heart Attacks Run In Families
How Is Afib Related To Stroke
AFib increases a persons risk for stroke. When standard stroke risk factors were accounted for, AFib was associated with an approximately fivefold increased risk of ischemic stroke.6 AFib causes about 1 in 7 strokes.7
Strokes caused by complications from AFib tend to be more severe than strokes with other underlying causes. Strokes happen when blood flow to the brain is blocked by a blood clot or by fatty deposits called plaque in the blood vessel lining.
Risks Associated With Atrial Fibrillation
The main danger of AF is the associated risk of stroke. This is present even if AF is only experienced some of the time, and whether or not the AF shows symptoms. One in every three strokes is linked to AF, and AF-linked strokes are more severe than other strokes. People with AF are also five times more likely to have a stroke compared to those who do not have AF.6
The risk of an AF-associated stroke occurring is also higher if you are older than 65, and if you have high blood pressure or diabetes, or have had a previous stroke, or if you have heart failure.
Other heart problems, such as heart attack and particularly heart failure, are also more likely to occur in people with AF.
People with AF are also at increased risk of dementia. This link is independent of stroke and other risk factors, although whether the link is causal is not yet known.
Read Also: What Happens To Heart Rate During Heart Attack
Read Also: Heart Valve Replacement Surgery Recovery Elderly
